Gitlab
Trigger a build of your website on Gitlab directly from the DatoCMS UI, and get a notification of the status of the build when it completes
This guide assumes you have a working static website project on your machine integrated with DatoCMS
If that's not your case, you can return to the previous sections of this documentation to see how to properly configure the DatoCMS administrative area and how to integrate DatoCMS with your favorite static website generator.
Create your Git repository
DatoCMS supports both Gitlab.com and self-hosted instances of Gitlab CE. The first thing to do is to initialize a new Git repository on your website local directory:
$ git init$ git add .Commit the files that you've staged in your local repository.
$ git commit -m 'First commit'Now create a new repository on Gitlab. Once done, copy the remote repository URL. In Terminal, add the URL for the remote repository where your local repository will be pushed.
$ git remote add origin YOUR_GITLAB_REPOSITORY_URLNow, it's time to push the changes in your local repository to Gitlab.
git push -u origin masterNow that your project is up and running on Gitlab, let's configure a Gitlab Pipeline that will publish your website on S3 after each further Git push.
Enable Gitlab Pipeline
GitLab offers a continuous integration service out of the box. If you add a .gitlab-ci.yml file to the root directory of your repository, then each commit or push triggers your CI pipeline.
Add the DatoCMS API token as environment variable
Reach the Settings > CI/CD Pipelines settings page of your project, and in the Variables section, add an environment variable called DATO_API_TOKEN containing the read-only API token of your DatoCMS administrative area:
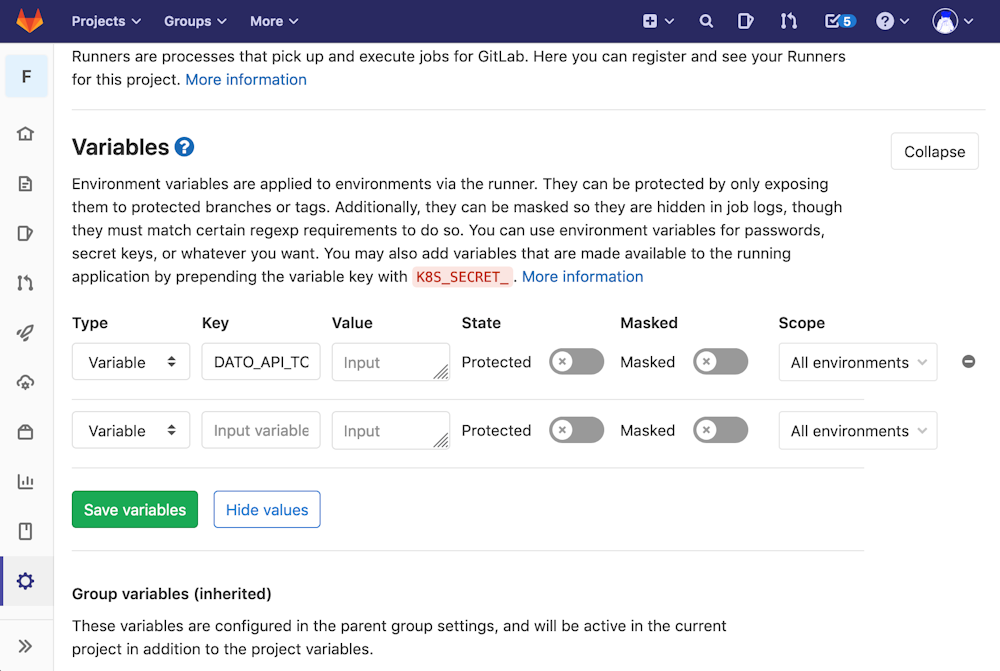
You can find the API token in the Admin area > API tokens section:

Configure .gitlab-ci.yml
The .gitlab-ci.yml file tells the GitLab runner what to do. By default it runs a pipeline with three stages: build, test, and deploy. You don't need to use all three stages; stages with no jobs are simply ignored.
Please refer to the official Gitlab documentation to learn everything regarding how to configure your build.
Jekyll
Here is an example .gitlab-ci.yml that you can use to run your build using Jekyll:
# requiring the environment of Ruby 2.3.ximage: ruby:2.3
# add cache to 'vendor' for speeding up buildscache: paths: - vendor/
before_script: - pip install awscli - bundle install --path vendor
variables: S3_BUCKET_NAME: "yourbucket"
# add a job called 'deploy'deploy: script: # first dump all the remote content as local files - bundle exec dato dump # then generate the website - bundle exec dato jekyll build # copy the /public folder to S3 bucket - aws s3 cp ./ s3://$S3_BUCKET_NAME/ --recursive --exclude "*" --include "*.html" only: - master # the 'deploy' job will affect only the 'master' branch